
Some businesses keep special journals like a purchase journal or sales journal, while others use one general journal to record their business transactions, which are later posted to the general ledger. It can be used for business, for school, for making a book, etc. These books are also where financial statements may be recorded. These books have so many things in common; this is why these two are easily thought to be the same. However, the same as their features are, they are still different from each other.

Everything To Know About Journal And Ledger Entries
The general ledger is a complete record of your business’s financial activity, sorting transactions by account, making it easy to generate reports and analyze your financial data. It is known as the principal book of accounting or the book of final entry. Usually, journals and ledgers are both prepared by both accountants and bookkeepers. First, they prepare the journal, then they transfer the entries into the ledger. The demand for a journal and a ledger in the accounting process helps businesses and professionals in the long run. They reflect the overall integration of the two content topics and their integration in accounting, both journal vs ledger for students who are beginners and working professionals.
The Pats have struggled in Denver in the playoffs. Here’s the record

The Journal is a book where all the transactions https://yello.gr/online-finance-accounting-courses/ are recorded immediately when they take place which is then classified and transferred into concerned account known as Ledger. In essence, the journal records transactions in chronological order, while the ledger groups transactions by account. In accounting, a journal is where we record detailed descriptions of all the financial transactions regarding a particular business.

AccountingTools
A ledger is an accounting book in which all similar transactions related to a particular person or thing are maintained in a summarized form. If your software has a “payment type” field, treat it as metadata for reporting, not as the driver of debits/credits. When your bookkeeping system is API-driven, I still recommend keeping this T-account view in your debugging toolkit. When an entry “looks right” but balances feel off, T-accounts usually reveal the mistake in seconds. If you post income tax as an expense in a proprietorship, you’re mixing Foreign Currency Translation business performance with owner-level obligations.
- It helps track balances more easily as journal entries are grouped.
- When it comes to journals, ledgers, and double entries in general, it’s often paramount to get the basics right.
- From the ledgers, financial statements are prepared, crucial for reporting and making decisions.
- Recording and tracking uncommon transactions like depreciation, bad debt, and the sale of assets are made easier with journals.
- A Ledger is a principal book of account, and its primary purpose is to transfer transactions from a journal and then classify it into separate accounts.
Preparation of trial balance and financial statements
In a double-entry system, all transactions are recorded chronologically. A ledger also called a principal book, records all transactions in such a way that, for example, if in a business cash is used to purchase a building, then the cash balance of the business firm reduces. Meaning, whatever has taken place inside every transaction (whoever attended, the minutes of the discussion, etc.) should be written down in the journal.
The general ledger is considered the central repository for accounting transactions recorded. In a journal, transactions are recorded regularly and date-wise which helps in checking transactions easily and quickly. A summary explanation of the transaction, known as narration, is also included in the journal.

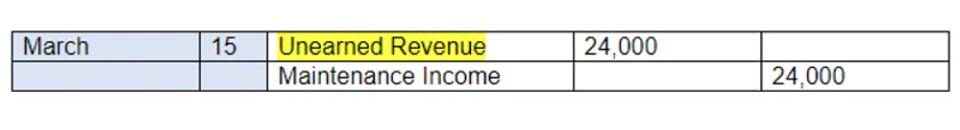
Bookkeeping is the backbone of any financial system, and both the journal and the ledger are core components of this process. While they serve different functions, they are equally vital in maintaining transparent and traceable records. This is the most general journal and is utilised for entries that don’t fit into the other accounts. Examples are adjusting entries, correcting errors, depreciation, provisions, and opening balances. To reflect both the outgoing expense and the source from which it was financed, the general ledger covers this transaction with dual entries in the expense account and accounts payable.
- UCF split two meetings with Colorado last season but lost by 13 on the road in the middle of their season-defining, seven-game slide.
- Primary book of accounting or the book of original/first entry.
- Figure 1, Panel A, describes a transaction, and Panel B shows how this transaction is entered in the journal.
- The Ledger gives a summary of all transactions for each account that have been noted in the Journal.
- This makes it easy to trace specific transactions, for example, for auditing purposes or if you need to check any discrepancies in your financial information.
- An adjusting journal entry is still a journal entry, with the only differentiating factor when the entry is done.
Use Wafeq to keep all your expenses and revenues on track to run a better business. You don’t need to worry about any of this, but now you’ll understand if your accountant mentions your sales ledger or purchases ledger to you. The General Ledger, which is just a list of every transaction you’ve ever made, arranged by account, is still present in Wafeq, even though it’s no longer pages in a large, leather-bound book. Transactions should be recorded in a Journal to be viewed chronologically. Ca’Lil Valentine scores from 6 yards out to give Illinois its first lead. The play was set up by a couple of long pass plays from Luke Altmyer to Hudson Clement (21 yards) and a trick play from Hank Beatty to Tanner Arkin (28 yards).
